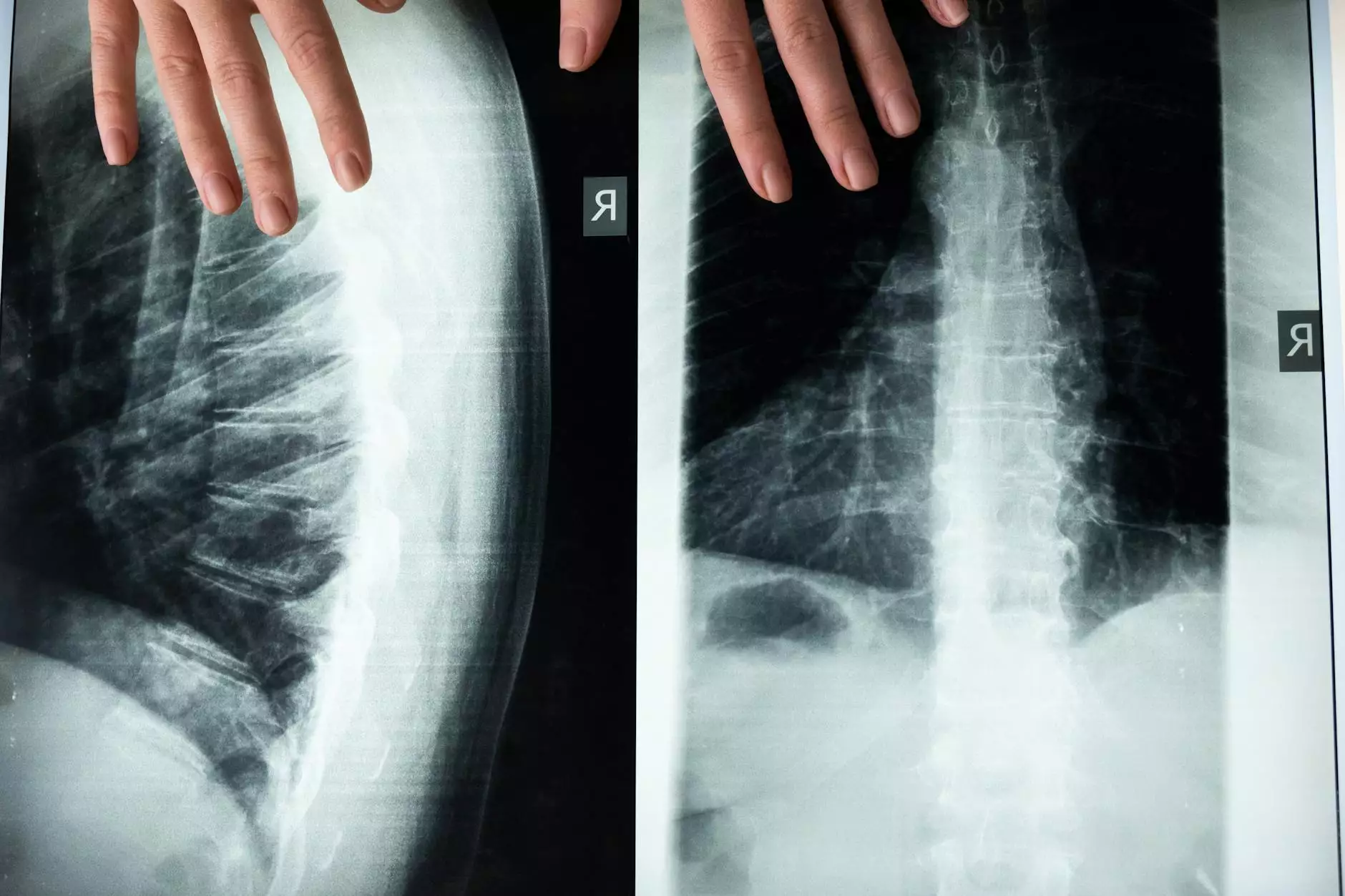
The Role of T4 Lesion in Health and Medical Fields
The study of T4 lesions in the medical field provides critical insights into various health issues, particularly those affecting the spine and the nervous system. T4 lesions refer specifically to abnormalities found in the fourth thoracic vertebra, which can have significant implications for an individual’s health. In this article, we will delve into the nature of T4 lesions, their causes, symptoms, importance in diagnosis, and management strategies.
Understanding T4 Lesion
The term T4 lesion encompasses any pathological condition affecting the fourth thoracic vertebra (T4) in the spinal column. This area is crucial as it does not merely support the rib cage but is also vital for protecting the spinal cord that runs through the vertebral column.
Types of T4 Lesions
- Traumatic Lesions: Resulting from injuries or accidents.
- Degenerative Lesions: Caused by wear and tear, often associated with aging.
- Inflammatory Lesions: Resulting from infections or autoimmune conditions.
- Neoplastic Lesions: Caused by tumors, which can be benign or malignant.
Causes of T4 Lesion
T4 lesions can arise from a variety of causes, ranging from traumatic injuries to disease processes. Understanding these causes is essential for effective prevention and treatment. The following factors may contribute to the development of T4 lesions:
- Trauma: Fractures or dislocations of the T4 vertebra can occur due to accidents, falls, or sports injuries.
- Osteoporosis: A condition that weakens bones and increases the risk of fractures.
- Tumors: Both primary and secondary tumors can develop in or affect the T4 vertebra.
- Infections: Conditions such as spinal tuberculosis (Pott's disease) can lead to lesions in the thoracic region.
- Inflammatory Diseases: Conditions like ankylosing spondylitis may also result in T4 lesions.
Symptoms of T4 Lesions
The symptoms associated with T4 lesions can vary depending on the underlying cause, as well as the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Localized pain in the upper back, which may radiate to other areas.
- Numbness or Tingling: These sensations can occur if nerve roots are compressed.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the arms or trunk can be indicative of severe lesions.
- Reduced Mobility: Stiffness and restricted motion in the thoracic region may be experienced.
- Postural Issues: Abnormalities in posture can develop due to chronic pain or spinal deformity.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Diagnosing T4 lesions early is crucial for effective management and treatment. Healthcare professionals can utilize several diagnostic methods to evaluate the condition:
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Diagnostic imaging plays an essential role in identifying T4 lesions. Common imaging techniques include:
- X-rays: Useful for detecting fractures or structural abnormalities.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of spinal structures and soft tissues.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: Useful for assessing complex fractures or lesions that might not be visible on X-rays.
Management and Treatment Strategies
The management of T4 lesions depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Treatment strategies can be categorized into non-invasive and invasive approaches:
Non-Invasive Treatments
In many cases, conservative management is effective for addressing T4 lesions. Non-invasive treatments include:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises can help in strengthening the muscles around the affected area and improving mobility.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractors can provide treatments like spinal manipulation to alleviate pain and improve function.
- Bracing: Supportive braces may be recommended for those with fractures or degenerative conditions to stabilize the spine.
Invasive Treatments
If conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if the lesions are severe, more invasive treatments may be necessary:
- Surgery: Surgical interventions may include decompression, stabilization, or removal of tumors from the T4 area.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may help to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Long-term Outlook and Prevention
Understanding the long-term outlook for individuals with T4 lesions is vital. Many people with less severe lesions can manage their symptoms effectively with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications. Preventing T4 lesions involves:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can strengthen the back and reduce the risk of injuries.
- Nutritional Support: Ensuring adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D can strengthen bones and joint health.
- Safety Measures: Using safety equipment during high-risk activities and maintaining a safe home environment to prevent falls.
Conclusion
In conclusion, T4 lesions represent a significant area of concern within the health and medical fields, especially for those affected by spinal issues. Through early diagnosis, comprehensive understanding of the underlying causes, and appropriate management strategies, individuals can navigate the challenges presented by these lesions. Whether you are a patient, a healthcare provider, or anyone interested in spinal health, awareness and education about T4 lesions are key to improving outcomes and maintaining a better quality of life.
For further information and professional assistance regarding T4 lesions, do not hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals or specialists at IAOM-US, where comprehensive care and expert advice are at your disposal.